Matrix Operations Exercise
The following matrices are given:
Questions
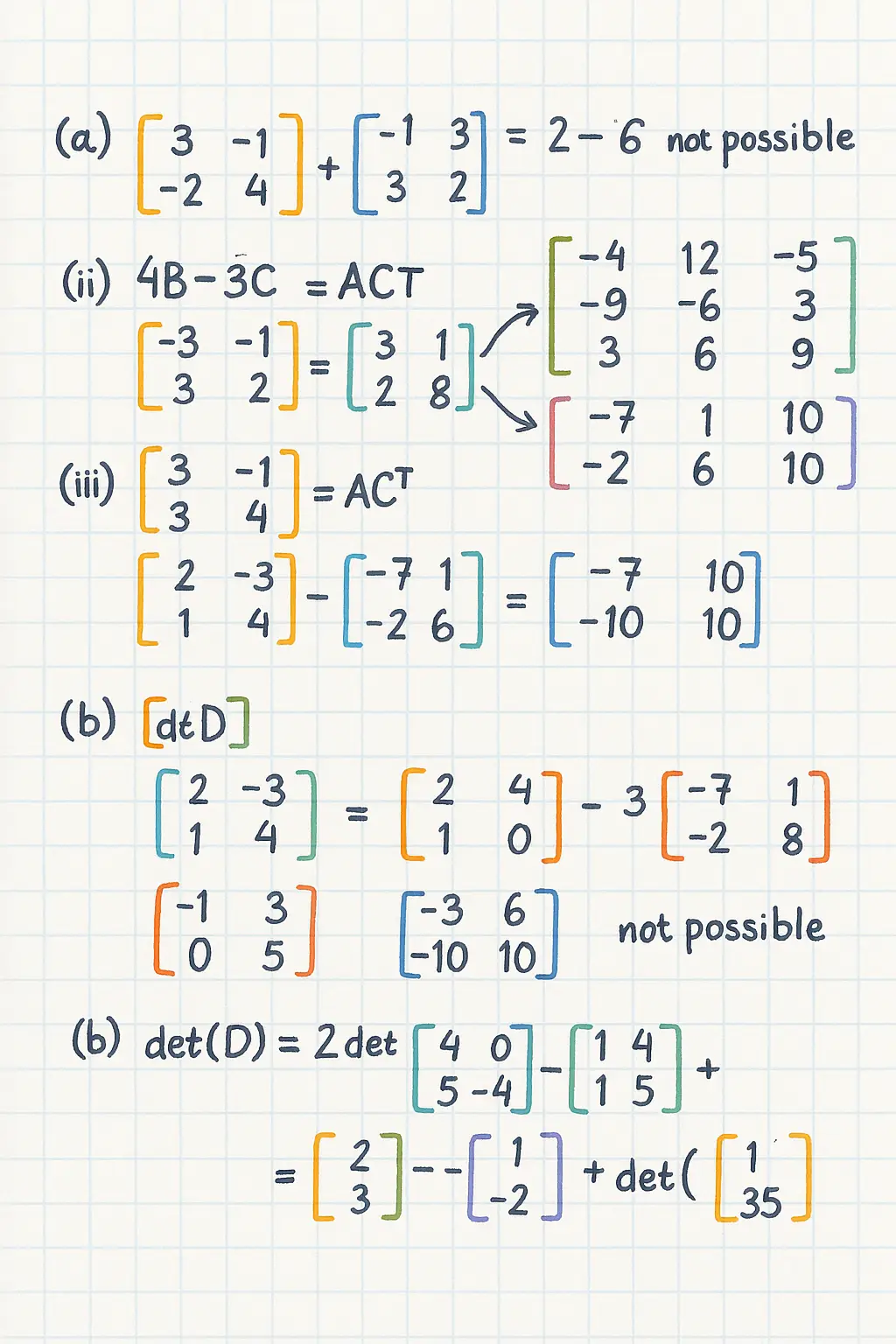
(a) Perform the following operations where possible:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(b) Calculate the determinant of matrix and explain whether the matrix is invertible.
Solutions
(a) Matrix operations
(i)
First, compute :
Matrix is , is .
🚫 Operation not possible (cannot subtract matrices of different dimensions).
(ii)
First, compute :
Compute :
Now subtract:
✅ Answer:
(iii)
First, compute :
Now multiply (3×2) by (2×2):
Multiply:
First row:
Second row:
Third row:
So:
✅ Answer:
(iv)
Matrix is , matrix is .
🚫 Operation not possible (inner dimensions do not match: and ).
(b) Determinant of matrix
Matrix :
Use cofactor expansion (along the first row):
Calculate minors:
Now compute:
✅ Answer:
Since , matrix is invertible.
Final Answers
- (a):
- (i) : Not possible
- (ii)
- (iii)
- (iv) : Not possible
- (b):
- , so matrix is invertible.